fat thickness measurement|how to measure body fat : fabrication In the abdominal area, measurement includes two fat layers, the superficial abdominal fat thickness (SFTa) and deep abdominal fat thickness (DFTa), in the first third of the image (⅓), considering the first 8.3 cm that is visible [10]. webРазмер: 3.99 MB, Длительность: 3 мин и 2 сек, Битрейт: 192 Kbps. с łđ Privet Privet 2009 St Sub Español. Mp3sax. . PRIVET PRIVET 2009 ST С łĐ Letra En Español Y Ruso Con Pronunciación. 01:40 2.19 MB 0.9K .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Panama - AF Sporting San Miguelito - Results, fixtures, squad, statistics, photos, videos and news - Soccerway. Bahasa - Indonesia; Chinese (simplified) Deutsch; English - Australia; . San Miguelito Country Panama Phone +507 230 0237 E-mail [email protected]. Venue Name Estadio Los Andes City San Miguelito Capacity .
A caliper measures the thickness of a “pinch” of skin and the fat beneath it in specific areas of the body (torso, thighs, front and back of the upper arm, and under the shoulder blade). Equations are used to predict body fat percentage . In the abdominal area, measurement includes two fat layers, the superficial abdominal fat thickness (SFTa) and deep abdominal fat thickness (DFTa), in the first third of the image (⅓), considering the first 8.3 cm that is visible [10].
Measuring the thickness of skinfolds in different areas of the body can help a person estimate their body fat percentage. According to the American Council on Exercise , this method provides . Skinfold calipers measure the thickness of your subcutaneous fat — the fat underneath the skin — at certain body locations. Measurements are taken at either 3 or 7 different sites on the body.This single measurement is a reasonably accurate predictor of overall carcass fatness; however, to improve the accuracy of the predictions of overall carcass fatness, the fat thickness measurement usually is adjusted up or down by the grader to account for visible differences in the distribution of external fat in other areas of the carcass. For body fat measurement, determining body fat composition by measuring the thickness of skinfolds is cost effective, requires minimal equipment, and is a practicable method of determining body fat in everyday clinical practice [8,9]. Using a suitable equation, fat-free mass (FFM) and fat mass (FM) can be calculated [10,11]. Despite great care .
In addition, B-mode ultrasound may be an alternative method for measuring subcutaneous fat thickness (SFT) and then estimating body composition from the measured SFT. In the 1980s, Kuczmarski et al. [18] reported a significant relationship between body density (BD) by underwater weighing and SFT obtained by ultrasound.
Echocardiographic EFT measurements of patients with IBD were significantly higher than those of the normal population, which may be associated with an increased subclinical atherosclerosis risk in these patients. . (c-IMT) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). Epicardial fat thickness (EFT) strongly influences both the formation .The mean difference in fat thickness between A-mode and B-mode was <0.7 mm at all sites except the calf (1.2 mm) CONCLUSION: With the exception of the suprailiac site, both A-mode and B-mode ultrasound are equally capable of providing measurements of subcutaneous fat thickness with an accuracy of <1 mm at most sites.
The skinfold method uses specially designed calipers to measure the thickness of skinfolds that are pinched from several specific locations on the body, as seen in this skinfold demonstration video [1].The skinfold thicknesses are correlated with body fat percentage using tables or equations that were produced by making both displacement and .
US is the only imaging method capable of measuring both the thickness of the fat layer with and without the embedded structures14–16,28. The applicability of this novel approach in groups with overweight and obesity has been shown by Störchle et al.17. Eight sites are used to represent the trunk (three), the arms (two), and the legs (three). .
Calculating Percent Body Fat Using Skinfold Measurements. You can measure body fat percentage using a variety of different approaches. One of the most common methods involves determining the thickness of subcutaneous fat. The approach recommended by Jackson, A.S., Pollock, M.L., and Siri et al. can be used to accurately calculate percent body fat. The mean difference in fat thickness between A-mode and B-mode was <0.7 mm at all sites except the calf (1.2 mm) CONCLUSION: With the exception of the suprailiac site, both A-mode and B-mode .
Participants and measurement sites. The university’s Institutional Review Board approved the study (protocol #7560). The subcutaneous fat thickness of a cohort of 6 cadavers (3 male, 3 female .purpose: to estimate body fat level by the measurement of skinfold thickness equipment: skinfold calipers (e.g. Harpenden, Slimglide, Lange), tape measure, marker pen, recording sheets.Read the Skinfold Guide for a comparison of available calipers.. pre-test: Explain the test procedures to the subject.Perform screening of health risks and obtain informed consent.
They also found that ultrasound was superior to the caliper method in measuring fat thickness in obese persons. Over the past 30 years, several studies have developed prediction equations for estimating BD and % body fat (% BF) from ultrasound measured SFT for healthy young and middle-aged adults [19], [20], [21] and young sports athletes [22 .We sought to develop % BF prediction equations for middle-aged and older adults using ultrasound subcutaneous fat thickness (SFT). Methods: A cross-sectional study of Japanese adults (n = 414, 50-79 years) where 276 subjects were randomly assigned to a model development group and the other 138 subjects were assigned to a cross-validation group.
US is the only imaging method capable of measuring both the thickness of the fat layer with and without the embedded structures14–16,28. The applicability of this novel approach in groups with overweight and obesity has been shown by Störchle et al.17. Eight sites are used to represent the trunk (three), the arms (two), and the legs (three). .Abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness measurement by ultrasound We used an ACUSON S3000 US System with 9L4 Transducer (4-9 MHz) (Siemens Medical Solution, Mountain View, USA) for the measurements. US and DXA measurements were performed on the same day, with no clinical intervention in between. The physician who measured the fat thickness was . Since skinfold thickness may be a better predictor of percent body fat, studies have found that adolescent skinfold thickness is a better predictor of high body fatness in adults than BMI. A body composition assessment can also help determine any health problems that your client may have.
If you are going to use callipers as a form of measurement it is recommended you practice your skill in measuring skinfolds on between 50-100 ‘practice’ participants to develop your proficiency. Procedures for skinfold measurement: You need to firmly grasp a fold of your client’s skin between your thumb and index finger and lift this up.
Measurement of mean subcutaneous fat thickness: eight standardised ultrasound sites compared to 216 randomly selected sites . The mean SAT thicknesses M I,2160 and M E,2160 (mean of 2160 SAT . The use of ultrasound to measure fat thickness in humans dates back to the mid-1960s [12, 13]. Despite a nearly 50-year history of ultrasound being used to measure subcutaneous adipose tissue, this technology seems to be used far less than the previously mentioned methods for body composition assessment, and many students, researchers, and .
To ensure a more accurate measurement of abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness, both transverse measurement (MASFT) and coronal measurement (RFASFT) of the abdominal subcutaneous fat thickness were used. Prior studies have found a higher degree of obesity to be related to higher serum levels of lipids [7,16,17]. SC-fat thickness at the level of the umbilicus was used to estimate SC adipose mass and variations of fat distribution along the vertical axis of the body may limit the accuracy of this measure. Since men tended to be older than women in this study, the gender-related associations between perirenal fat and extra-renal fat must be interpreted .
Average thickness of the supraorbital region skin is 1.67mm and superficial fat is 1.82 mm. Average thickness of the infraorbital area skin is 1.97mm and for superficial fat it’s 4.93 mm. In the perioral region, the average thickness of skin is 1.82mm and superficial fat is 5.14 mm. In the temple, the average skin thickness is 1.65mm and . When comparing ultrasonic measurements, the Renco, SFK, Medatta and Meritronics, with optical measurements taken at the abattoir, Hawe (1994), using only 24 pigs found that, in agreement with Greer et al. (1987), the Medatta ultrasonic probe did not give a good prediction of the depth of subcutaneous fat on the live pig.In addition, Pomar et al. (2001) .Circumferences of the trunk or limbs reflect amounts of underlying FFM and FM. Skinfold thickness describes the amount of subcutaneous fat when the skin is pinched by specialized calipers (Figure 3.1).Combinations of circumference and skinfold thickness measurements are utilized to predict body composition and have been validated with comparison to reference .
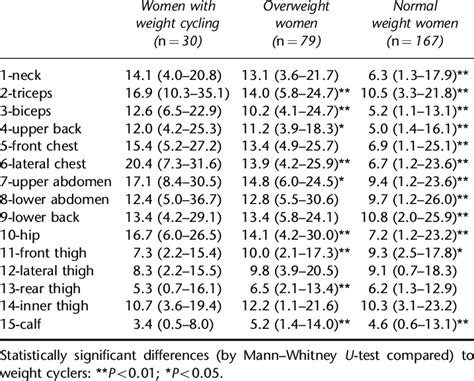
subcutaneous fat thickness chart
subcutaneous fat thickness calculator
Resultado da The Sporting San Miguelito Women Football Club page on Scorebar offers live scores, results, standings, head to head matches, match details and .
fat thickness measurement|how to measure body fat